Forces Acting on a Ladder Leaning Against a Wall
But the friction force is acted on the two points of the ladder which is in contact with the surfaces point A and B. In a free body diagram one shows all the forces acting on the ladder.
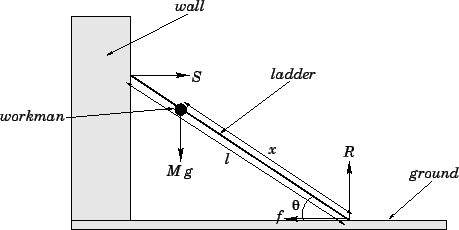
The weight of the workman.

. Students make predictions about the forces acting on a dynamic track ladder leaning against a smooth wall. A 1 b 3 c 5 d 4 e 7 If you choose the center of mass of the ladder as a fulcrum how many non-zero torques will be acting on the ladder. 25 A ladder is leaning against a wall.
The figure shows a ladder leaning against the wall on which a medieval knight is climbing. How many forces acting on the ladder. The weight of the person which acts a distance along the ladder.
The reaction at the ground. Additional activities include adding a weight to the track and accounting for the friction between the track and the wall. At top of the ladder there is a normal force due to the wall.
One approach by Mendelson 4 considers only the axial compression on the ladder in an idealized beam situation. A ladder is leant against the wall. The weight acts at the position of the workman and is directed vertically downwards.
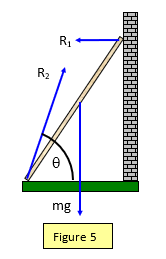
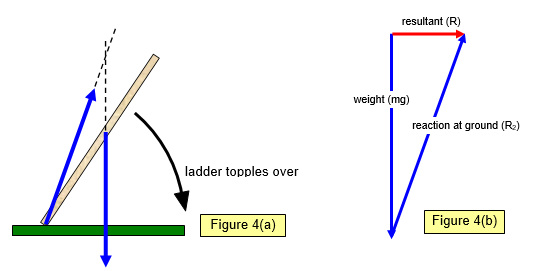
There are four forces acting on the ladder. The centre of mass of the ladder is in the middle of it. Find the minimum angle that the ladder can form with the floor not to slip down.
The forces on the ladder are. Check out my video on a ladder leaning again. And the frictional force due to the ground.
In that case according to the second law of motion the object will be in equilibrium 8 The vector sum of all the torques acting on the ladder as calculated about any axis must be zero. A ladder standing against a wall can be modeled as a uniform beam in static equilibrium. The weight of the ladder which acts half-way along the ladder.
Here I look at the moments of forces for a ladder resting in equilibrium against a smooth wall and ground and held by a tie to prevent it slipping. Persons weight that take into full account the normal and frictional reaction forces. But you can represent the force of wall on ladder by its components normal force and friction or by a single force vector that includes everything like they do in.
The coefficient of the static friction μ sw between the ladder and the wall is 03 and the coefficient of the static friction μ sf between the ladder and the floor is 04. The gravitational force is acting at the center of the ladder. 3 Normal reaction R_g on the ladder by the floor acting upward.
Figure shows the ladder resting against the wall having smooth surface and ground having rough surface. Only three forces contribute to this torque. And the reaction at the wall which acts at the top of the ladder.
The lever arms associated with these three forces are and respectively. Gravity force of wall force of floor. Acceleration due to gravity the ladder tends to move downward and right direction.
A more advanced treatment considers flexion 6. A ladder leaning against a wall is an example of a statically indeterminate structure for which the equations of equilibrium are insufficient to determine the reaction forces. The reaction at the wall.
There are torques due to these forces. In such problems the. Mvecg The force of gravity vecS The force from the wire vecN_1 The force from the ground at the base of the ladder vecN_2 The force from the edge of the box at which the ladder is leaning.
A ladder is leaning against the wall. They check their predictions using a Wireless 2-Axis Force Platform. A ladder leaning against a vertical wall.
Here I look at the moments of forces for a ladder resting in equilibrium against a smooth wall and rough ground. The conditions for equilibrium are the following A The vector sum of all the forces acting on the ladder must add up to zero. My initial thought relating to the forces was that there has to be four forces acting on the ladder.
1 weight of the ladder acting vertically downwardw 2 force of friction F_won the ladder by the wall acting upward. Note that the reaction force acts to twist the ladder in the opposite sense. At the base of the ladder there are two forces acting the normal force of the floor on the ladder and the frictional force.
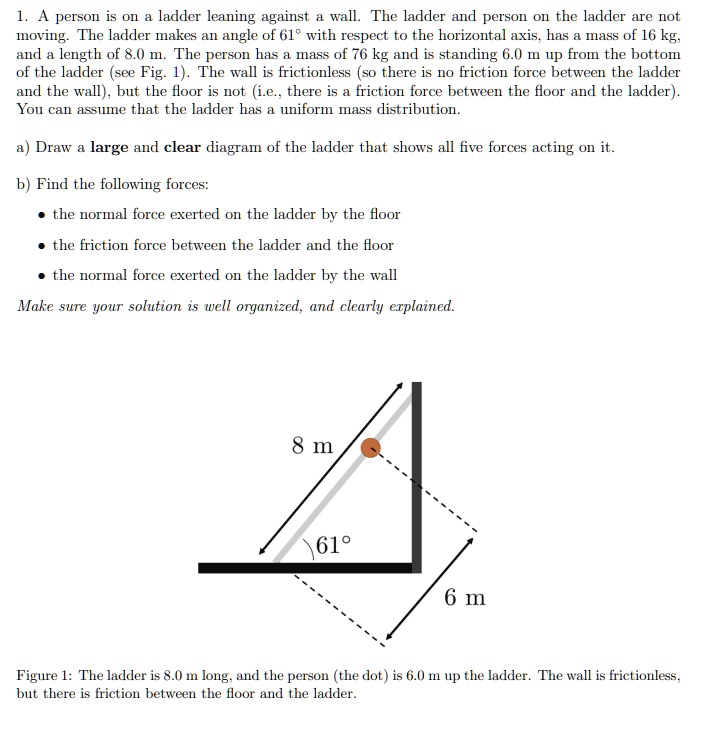
Solved A Person Is On Ladder Leaning Against Wall The Ladder And Person On The Ladder Are Not Moving The Ladder Makes An Angle Of 61 With Respect To The Horizontal Axis Has

Physics Reference A Ladder Rests In Equilibrium On Rough Ground Against A Rough Wall
A Ladder With Length L And Weight W Leans Against A Frictionless Wall With Height H Where H L If The Maximum Coefficient Of Static Friction Between The Ladder And The Floor Occurs

Moments Of Forces Ladder Leaning Against A Smooth Wall And Rough Floor 2 2 Youtube
A 5 0 M Long Ladder Has Mass 11 5 Kg And Is Leaning Against Frictionless Wall Making A 66 Angle With The Horizontal Coefficient Of Friction Between The Ladder And Ground Is 0 42 What

A Leaning Ladder Collection Of Solved Problems

The Open Door Web Site Ib Physics Conditions For The Equilibrium Of Three Non Parallel Forces

A Ladder With Length L And Weight W Is Leaning Against A Vertical Wall It Makes An Angle With The Horizontal Surface The Wall Is Frictionless The Coefficient Of Static Friction Between

Static Equilibrium Ladder Against Wall Youtube
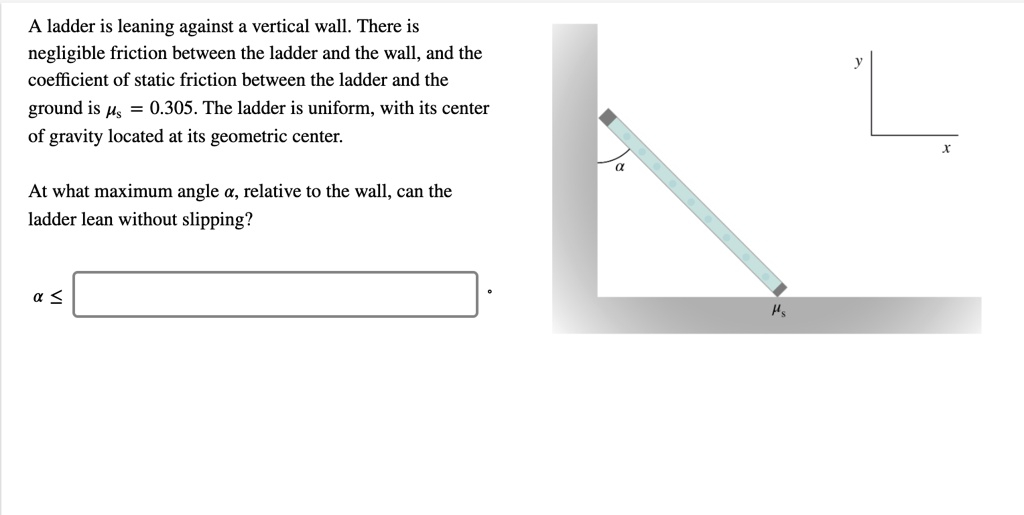
Solved A Ladder Is Leaning Against A Vertical Wall There Is Negligible Friction Between The Ladder And The Wall And The Coefficient Of Static Friction Between The Ladder And The Ground Is S

Newtonian Mechanics Reaction Forces Acting On A Ladder Against A Wall Physics Stack Exchange

Physics Mechanics Torque 7 Of 7 The Ladder Problem Should Be Cos 15 At End Youtube
A Ladder Rests Against A Frictionless Wall How Is The Force The Ladder Exerts On The Ground Related To The Weight Of The Ladder Why Quora
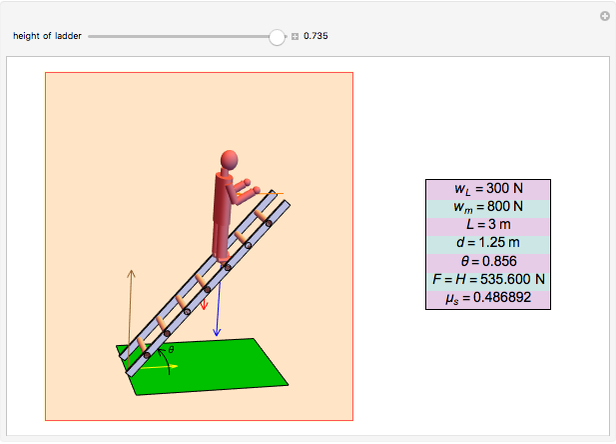
Forces Acting On A Ladder Wolfram Demonstrations Project

Homework And Exercises Leaning Ladder Reaction Force Physics Stack Exchange
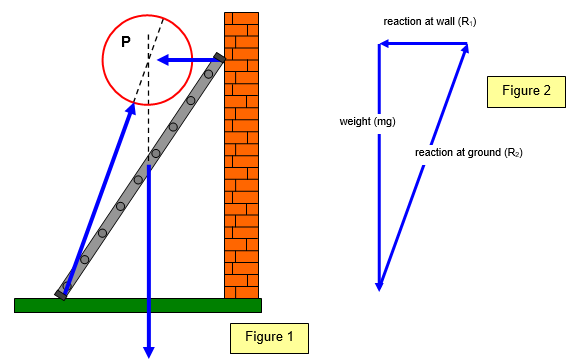
Comments
Post a Comment